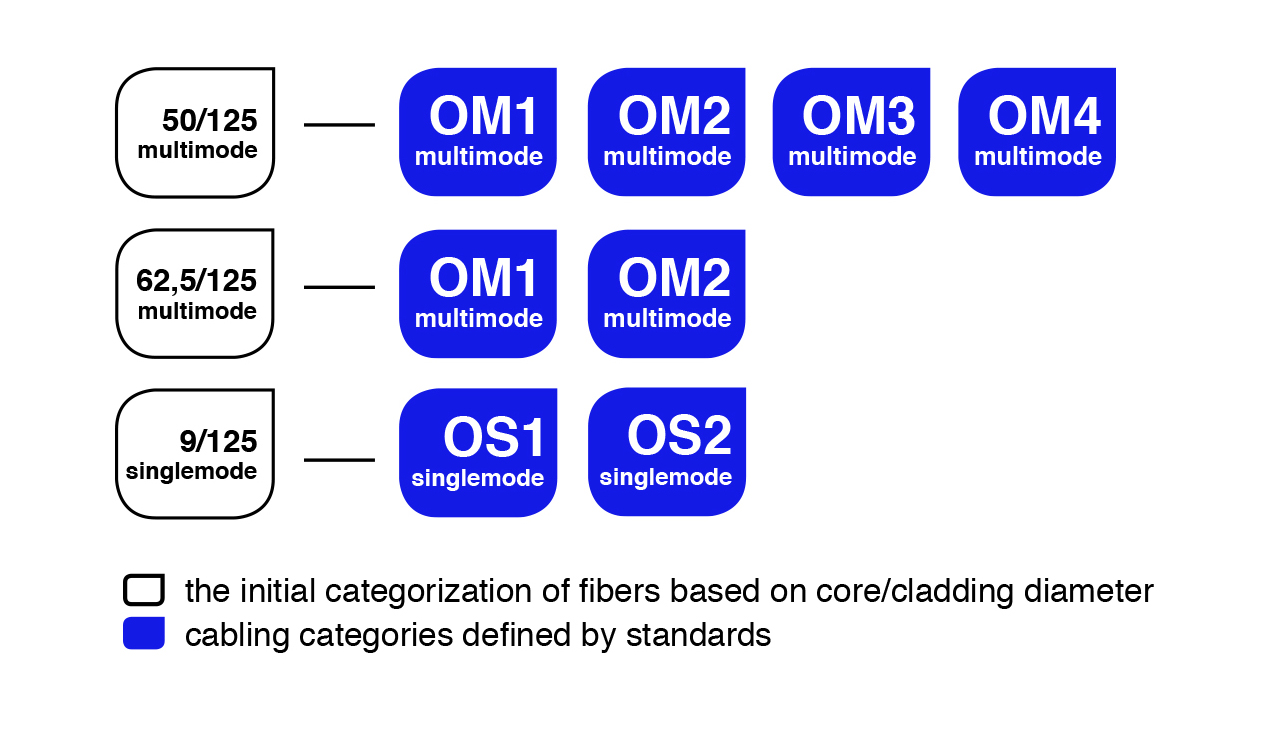
Recent high-speed protocols for optical cabling have triggered the development of new types of optical fibers and their new categorization. The initial categorization of fibers was based on glass core/cladding diameters of 50/125 μm, 62,5/125 μm or 9/125 μm. Modern fibers have different transmission characteristics despite identical glass geometry. International standards have therefore introduced a new classification based on the fibers’ performance level.
The diagram bellow illustrates the relationship between the initial categorization and the new categories as defined by standards:
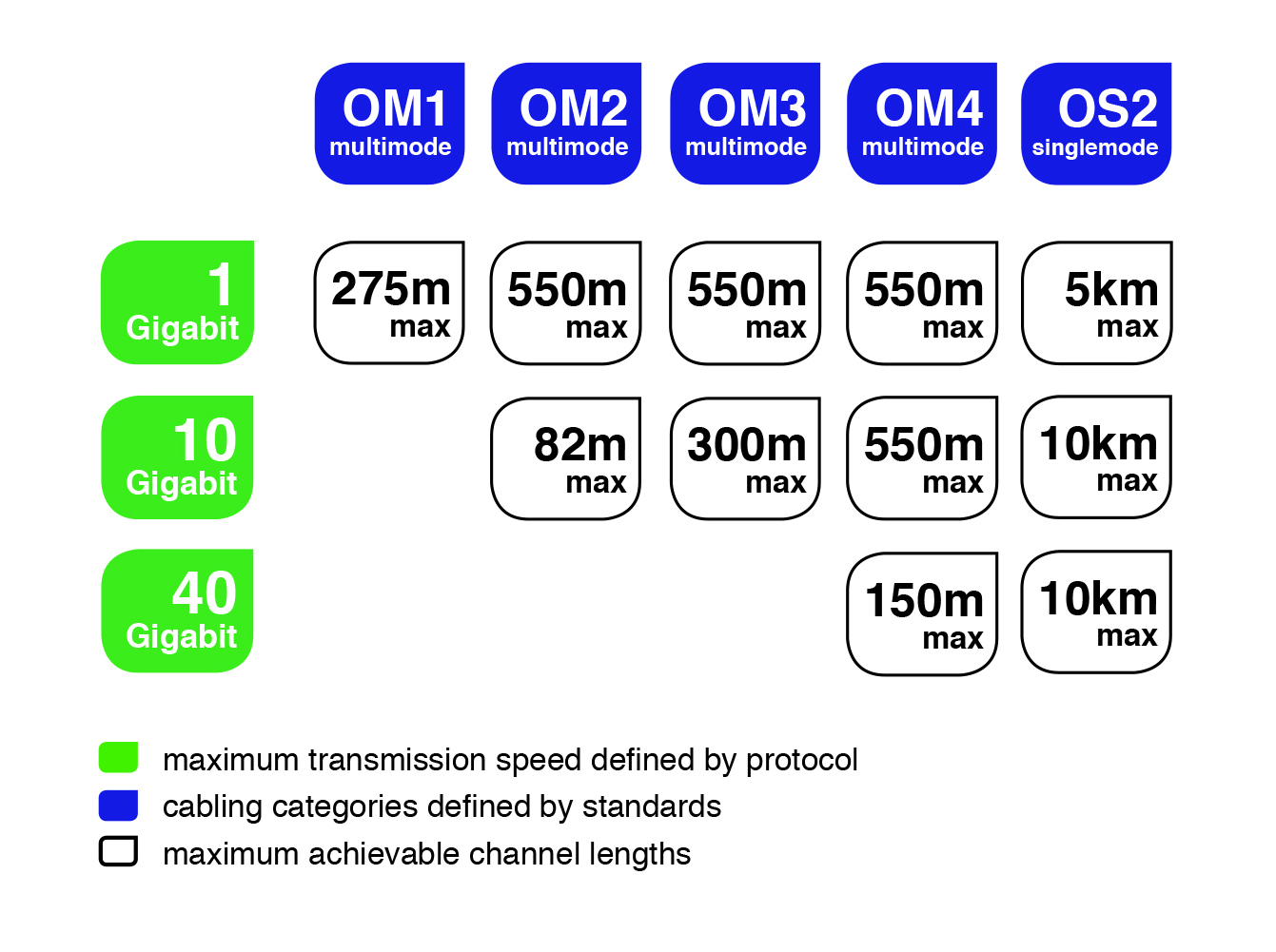
Performance level is determined by the maximum transmission speed. Protocols ensuring these transmission speeds are supported in each category over different channel lengths.
When choosing optical cabling it is necessary to keep in mind the desired transmission speed and the maximum channel length (the longest segment of cabling).
Diagram illustrating standardized transmission protocols (excluding proprietary applications) used in structured cabling aims to simplify the selection of a suitable optical fiber: